What is Cloud Computing? The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
Last Updated: February 2026
Stop buying servers. Rent them like a pro.
Introduction: The “Laptop” Problem
Imagine this scenario: You buy a powerful gaming laptop for ₹1,00,000 to edit videos.
- Month 1: You use it every day. Money well spent.
- Month 2: You get busy and don’t edit any videos. The laptop sits gathering dust.
- Year 3: The laptop is now slow and old. You need to buy a new one.
This is a bad investment. You paid for power you didn’t use all the time. Cloud Computing solves this. What if you could “rent” a Supercomputer for just 2 hours to edit your video, pay ₹50, and then return it?
That is Cloud Computing.
1. What is Cloud Computing? (The Definition)
Simple Definition: Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services (servers, storage, databases, networking, software) over the internet (“the cloud”).
The Core Idea:
- Old Way (On-Premises): You buy the cow to drink milk. (Buy Servers).
- New Way (Cloud): You buy milk cartons from the store. (Rent Servers).
Real-Life Examples:
- Google Photos: Your photos aren’t on your phone; they are on Google’s Cloud.
- Netflix: Movies aren’t on your TV; they are streamed from AWS Cloud.
2. A Simple Story: Ram vs. Ravi (On-Premises vs. Cloud)
To understand the value, let’s look at two startup founders.

Ram (The Old Way): Ram starts an online store.
- He buys 10 Servers (Cost: ₹10 Lakhs).
- He rents a room with AC to keep them cool (Cost: ₹20k/month).
- Problem: On Big Billion Day, 10 servers aren’t enough. The site crashes. Ram loses customers.
- Result: High Cost + High Stress.
Ravi (The Cloud Way): Ravi starts the same store using AWS.
- He clicks a button and launches 1 server (Cost: ₹0 upfront).
- On Big Billion Day, he clicks a button to launch 100 more servers instantly.
- The next day, he deletes them.
- Result: Low Cost + Zero Stress.
3. The Technology Behind It: Virtualization
This is the technical “Magic” that interviewers ask about.
How can Amazon give you a “server” in 2 seconds? Do they have a robot plugging in cables? No. They use Virtualization.
- The Physical Server: Amazon has a giant physical machine (300 GB RAM, 100 CPUs).
- The Hypervisor: This is software that slices that giant machine into tiny pieces called Virtual Machines (VMs).
- The User: You get one of those tiny slices. It looks like a full computer to you, but it’s just a file on Amazon’s disk.
4. Types of Cloud Deployment Models
Not all clouds are the same. There are 3 main types:
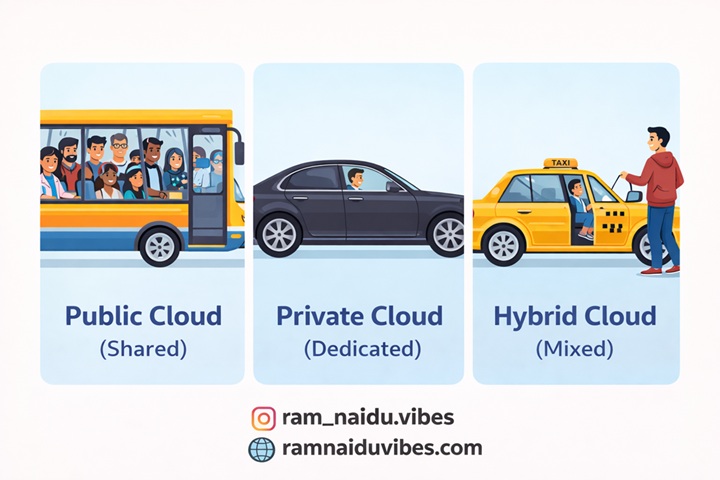
A. Public Cloud (The Bus)
- Description: Hardware is shared by many companies (Tenants).
- Example: AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure.
- Analogy: Like a Public Bus. You share seats with strangers. It’s cheap and efficient.
B. Private Cloud (The Car)
- Description: Hardware is dedicated to a single company.
- Example: Bank Servers, Government Data Centers.
- Analogy: Like your Personal Car. Only you drive it. It’s expensive but secure.
C. Hybrid Cloud (The Taxi)
- Description: A mix of both. Critical data stays private; web traffic goes public.
- Analogy: Like a Taxi. It’s a car (private space) but you pay for the ride (public service).
5. Cloud Service Models (IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS)
This is the most important concept for exams and interviews. Let’s use the “Pizza Analogy”.
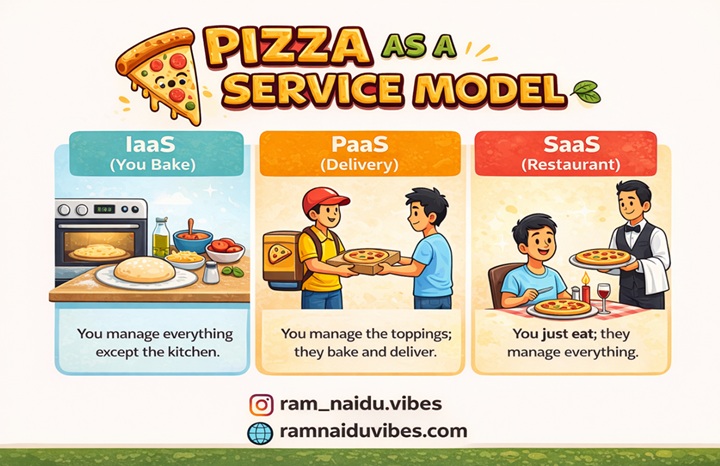
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- You get: The Kitchen, the Oven, and the Gas.
- You do: You bring the dough, cheese, toppings, and bake the pizza yourself.
- Technical: You rent the VM (EC2). You install Java, Tomcat, and your App.
- Examples: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- You get: A Pizza Delivery.
- You do: You just choose the toppings (Pepperoni or Veggie). The restaurant bakes it.
- Technical: You upload Code. AWS handles the OS, Java updates, and scaling.
- Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
- You get: A Pizza Restaurant experience.
- You do: You just go there and eat. No cooking, no cleaning.
- Technical: You just Log in. The software is already running.
- Examples: Gmail, Zoom, Salesforce.
6. Why AWS? (Amazon Web Services)
AWS is the market leader. Why?
- Global Infrastructure: AWS has data centers in 30+ regions (including Mumbai and Hyderabad).
- Pay-as-you-go: If you use a server for 10 minutes, you pay for 10 minutes.
- Services: They have 200+ services (Robotics, Satellite control, Blockchain).
7. Conclusion: Is Cloud a Good Career?
Look at the job market.
- Traditional IT Admin:
- Cloud Engineer / DevOps:
You don’t need a PhD to learn Cloud. You just need to be curious. Start by creating a Free Tier AWS Account and launching your first EC2 instance.
